Core Platform
Proprietary Platform Technology & Diversified Pipeline
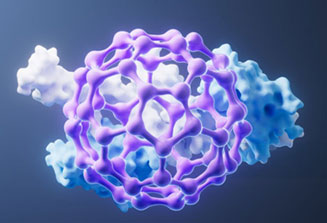
At the core of MediWound’s innovation is a proprietary platform based on a unique mixture of proteolytic enzymes, enriched in bromelain— derived from the stem of the pineapple plant. Using our exclusive enzyme enrichment technology, these bioactive compounds are carefully extracted, purified, and enhanced to achieve maximum therapeutic potential.
This platform serves as the foundation for both our approved product and our entire pipeline of biologic therapies in development. With multiple mechanisms of action, bromelain offers broad clinical applicability across various therapeutic areas.
Our mission is to lead a paradigm shift toward non-surgical solutions that redefine standards of care, with a current focus on therapies that promote and accelerate tissue repair.
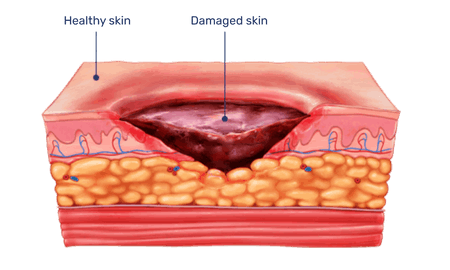
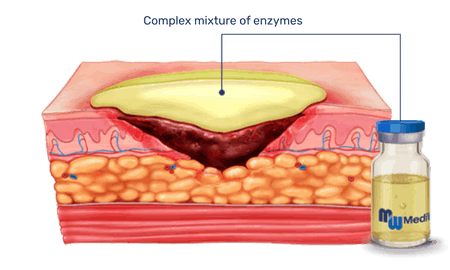
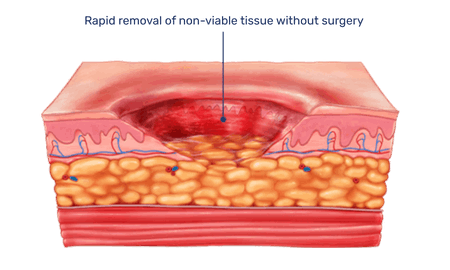
When topically applied to burns or wounds, the enzymes selectively break down non-viable tissue while leaving healthy, viable tissue unharmed.
Plant to Drug




Publications
NexoBrid®














EscharEx®